What is a cold room?
A cold room is a professionally insulated refrigeration chamber designed to generate and maintain low temperatures artificially. This cold storage is generally used on a large scale for storing temperature-sensitive products such as vaccines, pharmaceutical products, and perishable items. Cold rooms can vary in size from a small walk-in storage spaces to huge warehouses, depending on your application.
Factors to consider while designing cold rooms.
- Temperature range.
- Cooling capacity.
- External environment.
- Accuracy of control.
- Running costs.
- Storage capacity.
- Running cost.
Steps of cold room design.
Step one: site selection.
The supporting structures around cold rooms determine its design. These structures include a tool room, working room, or a packing and preparation room.
Step two: cold room storage capacity and temperature.
The size of cold rooms should be determined by the highest perceived storage amount throughout the year. This will help determine its height and length.
Step three: selection of cold room storage preservation materials.
Local climate conditions are a significant factor when determining the materials that you will use. The materials that you use should have good insulation and be economically practical.
Step four: selection of cold room storage cooling system.
The selection of the cooling system generally involves the choosing of the compressor and the evaporator. For example, small cold rooms will likely use a hermetic compressor while large cold rooms select semi-hermetic compressors.
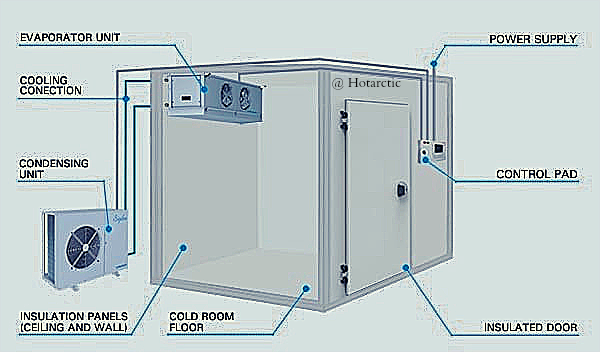
Components of a cold room.
-
Compressor.
The compressor is the component that runs cold rooms. It consumes most of the power of the cold room. The compressor raises the temperature of the refrigerant gas. In a nutshell, the compressor compresses the refrigerant gas.
-
Evaporator
The evaporator absorbs and cools the coils. The coils the heat from the space that is supposed to be cooled.
-
Condenser.
The condenser cools the refrigerant gas by removing heat from the refrigerant gas condensing the freon into a liquid.
-
Expansion valve.
Reduce the temperature pressure of the refrigerant gas. It controls the flow of the liquefied gas.
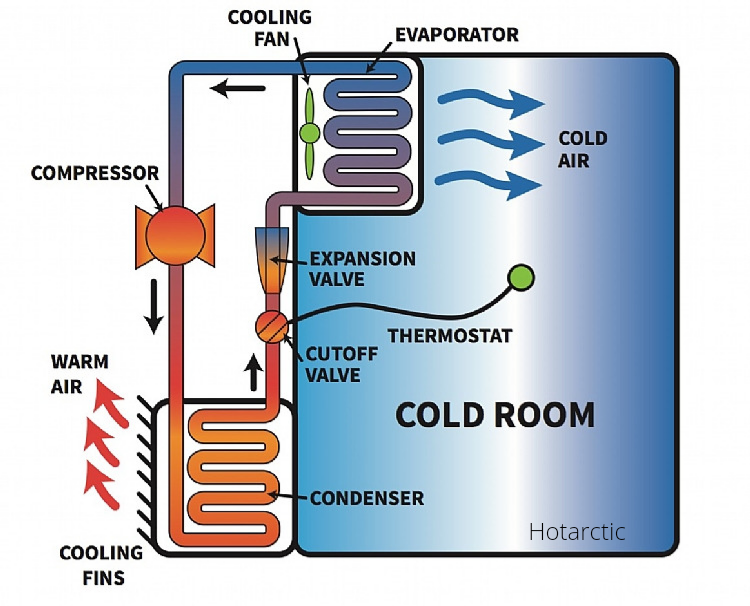
The cooling cycle.
Cooling starts with the refrigerant gas, moving through the compressor. The compressor compresses the refrigerant gas. This rises the pressure and temperature of the refrigerant gas. As the hot gas leaves the compressor into the evaporator, it comes into contact with the cool temperature in cold rooms which causes it to contract. Still, under high pressure, the refrigerant gas absorbs the heat from the space as it makes its way through the evaporator coils. The warm refrigerant gas then flows through the expansion valve /heat exchange, which removes the heat and sends the gas back to the compressor, and the cycle begins again.
Common types of cold rooms.
There are several options when it comes to the installation of cold rooms.
Cold rooms are classified according to:
i) The temperature range of the cold room.
-
Chiller cold rooms.
Chiller cold rooms generally maintain temperatures of between 1°C and 8° C. These cold rooms store pharmaceutical products, automotive parts, drink products, and other products that need to be chilled.
-
Walk-in freezers.
Freezer cold rooms keep temperatures between -5°C and -40°C. Walk-in freezers are best for storing products that need to remain frozen or to freeze previously chilled products.
A deep-freezing tunnel is a type of wall in the freezer where the temperature is between -30°C and -40°C. It freezes products individually using cold currents.
-
Combo cold room.
Combo cold rooms have a separate temperature zone for both chiller cold rooms and walk-in freezers. This type of cold room is perfect for products that require a wide range of temperature zones.
-
Ambient Temperature controlled atmosphere rooms.
Ambient rooms are areas, mostly used for preparation and packaging, that have a controlled temperature of between 10°C and 30°C.
ii) Design of the refrigeration system
-
Industrial chillers.
Industrial chillers are ideal for large quantities and bulky products. These types of cold rooms are large enough to accommodate not only people but trucks such as forklift trucks.
-
Remote cold room
A remote cold room involves an evaporator and a condensing unit, and parts such as an extension valve and an indoor pump regulator. The evaporator is installed inside the chiller the condensing unit is situated outside the storage space.
- Standard top mount refrigeration system
The evaporator and the condenser are merged into one unit. The design of this cold room allows for the retention of low temperatures over a long period.
-
Saddle mount cold room refrigeration system.
In the saddle mount cold room, the frameworks, which is pre assembled, are hung on the wall before the roof installation.
-
Penthouse cold room refrigeration system.
Penthouse cold rooms are designed to have sufficient space to allow strolling within cold rooms. The components of the cold rooms are installed, in a protected case with the evaporator, on the housetop and not inside the cold room
It has the advantage of expanded storage space and faster maintenance thus reducing downtime.
 Benefits of cold rooms.
Benefits of cold rooms.
- Cold rooms are energy efficient because they limit fluctuation in temperature.
- Cold rooms reduce the cost for sample storage.
- The potency of products such as vaccines and other sensitive items.
- There is an improvement in the reputation and reliability of industries due to high-quality end products.
- Cold rooms ensure that high-sensitive products and equipment are safe.
Maintenance of cold rooms.
Cold rooms require proper routine maintenance to promote efficient and effective cooling and avoid operational problems. Include the proper maintenance of evaporators, condensers, compressors, and expansion valves. The entire cold room system should undergo daily weekly, monthly, and quarterly preventive maintenance checks
- Check the level of the refrigerant gas daily.
- Ensure the condenser coils, evaporator fans are clean.
- Check the compressor for oil leaks.
- Calibrate cold room temperatures
- Check the evaporator for the possible formation of ice.
- Perform maintenance checks and overall functionality of the cold room (monthly, quarterly, yearly) as needed.
- Contact HotArctic heating and cooling to perform proper professional maintenance checks such as pressure difference, the capacity of the cold room pumps, and loose electric contact.
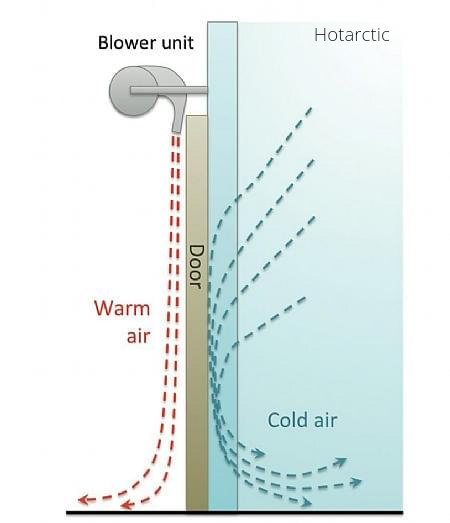
Always remember that for cold rooms to function correctly, air must be able to circulate the products inside. Therefore, when loading products into the cold room, you should always consider the airflow.
At HotArctic heating and cooling, we work to keep the all-important cold chain unbroken. We specialize in cold rooms, freezers, and chillers that meet all current standards for temperature regulation and insulation. With our market-leading prowess, we will deliver a solution that is reliable, accurate, and specially designed for your application.




This is the best piece of cold rooms everyone should know.
Hi, I want to say thank you for sharing this useful information its helpful to Me and every one who want to become a good technician.